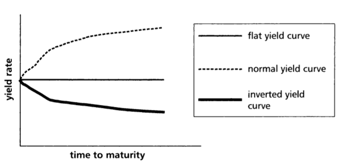
interest rate varies with the investment term.
Pure expectation theory:
view a sequence of short term bonds as a perfect substitute for a single longterm bond.
Liquidity preference theory:
invest money for a sequence of short period so that the money is frequently accessible.
issuers must offer long-term-bonds with higher rates, called liquidity premium
Preferred habitat theory:
Market segmentation theory:
not one market, divided into separate market for each term.
Yield curve to see one’s annual yield rate.

spot rate / zero-coupon rate is the annual effective interest rate earned by money invested at time 0 for a period of t years.
Treasury bills, matures of one year or less, zero coupon bonds, semiannual coupons.
K$ invested at time 0 grows to at time t.
if , investment grows to at time s.
The annual effective interest rate foe the interval is , such that
the theoretical forward rate / implied forward rate.
Assumption: compound interest, spot rate are all equal, if one spot rate changes, all change to remain a equal spot rate(parallel shifts).
Present Value
when , modified duration