Change in result in movement along the curve, quantity
demanded.
Change in result in movement along the curve, quantity
demanded.choose an appropriate level of output.
Total revenue , when depends on
(lower the
price to sell a larger amount of products)
total cost of producing is profits
Output choice , Take derivatives
Profits are max when
Second derivatives: , concave, mountain shape at maximum.
Example:
Demand function:
Solve for the Price
Given total cost =
Maximize profit Max
f.o.c:
When price does not depend on the quantity.
By maximizing profit,
Max total cost = Max
(firm takes price as given)
labor is easier to be changed than capital.
Make decision:
Positive quantity ()
MR=Short MC, p=Short MC
Shut down production at
p<SAVC
price is not lager enough to cover...
Example:
| shut down production | |
|---|---|
| quantity |
when choose to Shut down the production, meaning that
→
→
profits =
If price rises to
If price falls to , , MC upper-forwarding
slope
If price falls to , shut down, p <
Make decisions:
produce positive
,
exit the market at .
→
price is not high enough to cover the average costs.
market demand function
Only two goods:
Marshallian demand for x is
Market demand is the sum of all individuals marshallian demand.
Market demand
 Change in result in movement along the curve, quantity
demanded.
Change in result in movement along the curve, quantity
demanded.
Change in or , results demand curve for x shift.
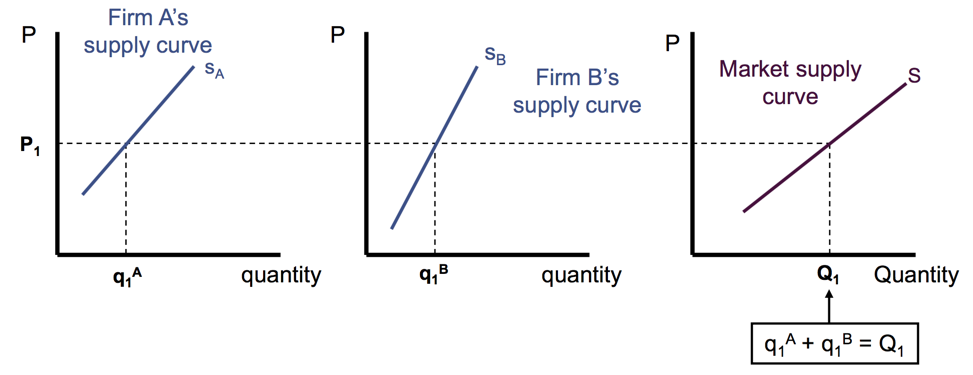
market supply function
Market supply is the sum of all individuals marshallian demand.
Market demand
Short run: market supply is the sum of the quantity supplied by existing Firms. (cannot enter ot exist the industry in the short run)
Long run un market supply s the sum of the quantity supplied by existing and entering firms.
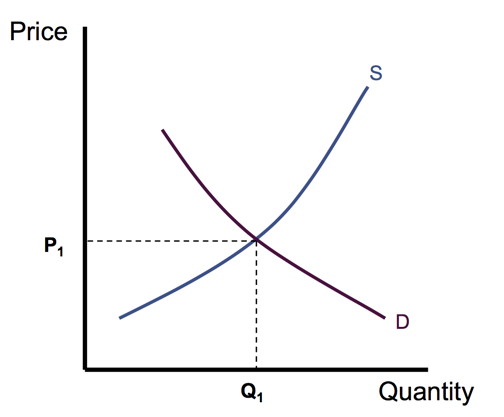
Equilibrium price, quantity demanded = quantity supplied.
Every one is on their optimal options.
At
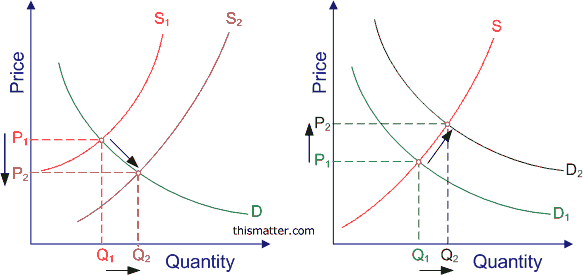
Many buyers experience an increase in the demands, the market demand curve will shift to the right.
| Shift in Supply | Shift in Demand |
|---|---|
| Equilibrium price falls and Equilibrium quantity rises. | Equilibrium price and quantity both rises. |
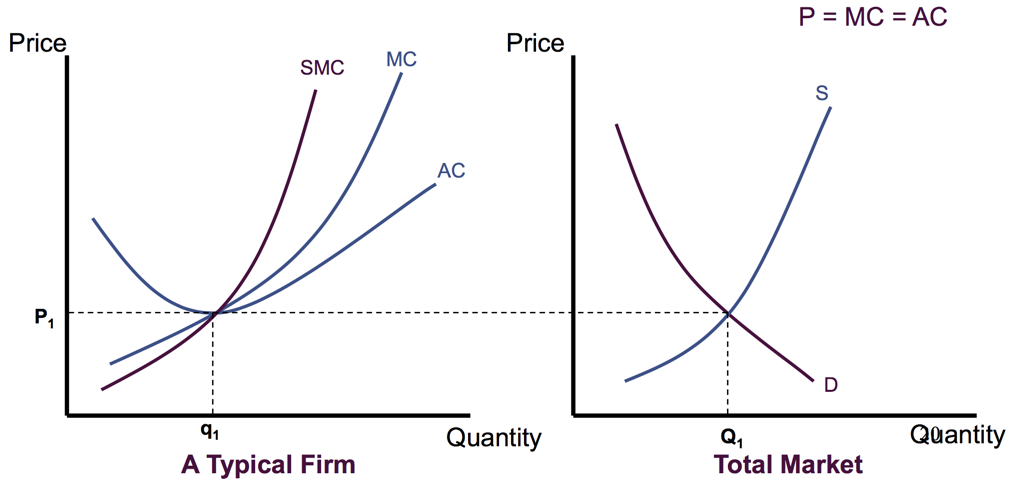
(market is in long-run Equilibrium.)
, operate at minimum
ZERO profits
(for
different cost functions, marginal firms are make zero profits)